6. Training neural networks I
1. Activation funcs
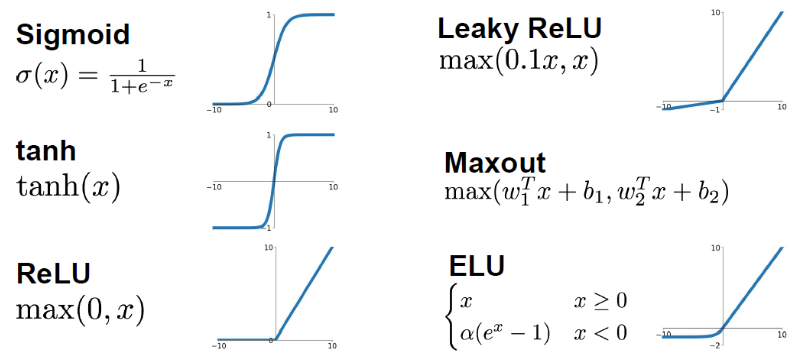
1.1 sigmoid
problems:
- big values neurons kill the gradients(大的x值会导致梯度为0)
- Not Zero-centered
- exp() is a bit compute expensive.
1.2 tanh
advantage:
- Zero-centered
problem:
- big values neurons kill the gradients(大的x值会导致梯度为0)
1.3 RELU
advantages:
- big values neurons don’t kill the gradients
- not compute expensive.
- Converges much faster than Sigmoid and Tanh
- More biologically plausible than sigmoid.
problems:
- Not Zero-centered
- If weights aren’t initialized good, maybe 75% of the neurons will be dead and thats a waste computation(为了解决这个问题,可以加个bias=0.01)
1.4 leaky RELU
advantages:
- Doesn’t kill the gradients from both sides.
- Computationally efficient.
- Converges much faster than Sigmoid and Tanh
- Will not die. 其中0.01也可以作为一个学习超参数
1.4 maxout
advantages:
- Generalizes RELU and Leaky RELU
- Doesn’t die!
problems:
- double the number of parameters per neuron
1.5 ELU
advantages:
- It has all the benefits of RELU
- Closer to zero mean outputs and adds some robustness to noise.
problems:
- exp() is a bit compute expensive.
1.6 In practice
- Use RELU. Be careful for your learning rates.
- Try out Leaky RELU/Maxout/ELU
- Try out tanh but don’t expect much.
- Don’t use sigmoid!
2. Data preprocessing
# Zero centered data. (Calculate the mean for every input).
# One of the reasons we do this is because we need data to be between positive and negative and not all the be negative or positive.
X -= np.mean(X, axis = 1)
# Then apply the standard deviation. Hint: in images we don't do this.
X /= np.std(X, axis = 1)
平均值两种计算方法,一种是减掉整个图片的平均值,一种是每个channel分别减去其平均值
3. Weight initialization
3.1 初始化为0
所有的神经元都一样了,更新的时候梯度全都一样
3.2 随机化
两种:
第一种在大型的神经网络上会导致后面的节点出现梯度消失的问题:
W = 0.01 * np.random.rand(D, H)
# Works OK for small networks but it makes problems with deeper networks!
第二种在大型的神经网络上会导致后面的节点出现梯度爆炸的问题:
W = 1 * np.random.rand(D, H)
# Works OK for small networks but it makes problems with deeper networks!
3.3 Xavier initialization
这种初始化目的是为了让每一层输出的方差一样,这样可以让信息更顺畅地在网络中流畅
W = np.random.rand(in, out) / np.sqrt(in)
但是使用relu的时候该方法会失效的
3.4 He initialization (Solution for the RELU issue)
解决Xavier的relu失效问题:
W = np.random.rand(in, out) / np.sqrt(in/2)
4. Batch normalization
该技术是为了让每一层的输入都是mean = 0, var = 1
一般该层是放在卷积之后,激活层之前的
步骤:
- 计算平均值以及方差
- 减去平均值,除以根号下方差+epsilon,epsilon的目的就是为了让分母不为0
- 接下来shift + scale:
Result = gamma * normalizedX + beta。其中gamma和beta都是可学习的超参数。目的是让NN可以学习各种概率分布,因为不一定都高斯分布是最好的。这样每一层就会更加灵活。
batch normalization的好处:
- Networks train faster.
- Allows higher learning rates.
- helps reduce the sensitivity to the initial starting weights.
- Makes more activation functions viable.
- Provides some regularization. Because we are calculating mean and variance for each batch that gives a slight regularization effect.
卷积层后面,都是每个activation map就算一个mean和var,不是几层一块算的!
常规的CONV和NN中batch normalization是best,但是循环的NN和rf中这还是热门的研究。
5. Baby sitting the learning process
- Preprocessing of data.
- Choose the architecture.
- Make a forward pass and check the loss (Disable regularization). Check if the loss is reasonable.
- Add regularization, the loss should go up!
- Disable the regularization again and take a small number of data and try to train the loss and reach zero loss. (You should overfit perfectly for small datasets.)
- Take your full training data, and small regularization then try some value of learning rate.
- If loss is barely changing, then the learning rate is small.
- If you got NAN then your NN exploded and your learning rate is high.
- Get your learning rate range by trying the min value (That can change) and the max value that doesn’t explode the network.
- Do Hyperparameters optimization to get the best hyperparameters values.
6. Hyperparameter Optimization
- Cross validation strategy
- It‘s best to optimize in log space
- Adjust your ranges and try again.
- Its better to try random search instead of grid searches (In log space)
Problems
- 怎么判断训练是否是更快了?